
WEGO Medical, a subsidiary of Weigao Group, is a leading medical device manufacturer。WEGO Medical, a subsidiary of Weigao Group
Oxygenator System
The venous blood with low oxygen content is oxygenated into arterial blood with high oxygen content to meet the needs of the patient during surgery.
WG2500A
The WEGO Membrane Oxygenator is an artificial organ designed for extracorporeal blood-gas exchange. The cardiopulmonary bypass oxygenator integrates the key functions of membrane oxygenation, temperature control, blood reservoir, filtration, and blood recovery into a single, comprehensive system.
This oxygenator uses a microporous hollow fiber membrane to achieve blood-gas exchange. Blood and gas come into indirect contact on both sides of the fiber menbrane wall, completing oxygenation and carbon removal through diffusion, effectively avoiding serum protein denaturation and better promoting extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.
WEGO oxygenator is an artificial organ that can exchange blood and gas. It integrates the functions of oxygenation, temperature change, blood storage, filtration, and blood recovery. Its main function is to oxygenate venous blood with low oxygen content. Becomes arterial blood with high oxygen content to meet the needs of the patient during surgery. 2021: Through comparison and application with imported products in total thoracic minimally invasive cardiac surgery, Weigao membrane oxygenator has no significant difference from imported products in terms of VAVD use, oxygenation performance, carbon dioxide removal and blood compatibility.
It uses hollow fibers with micropores as the medium for gas and blood exchange. The hollow fibers carry blood outside and gas inside. Gas and blood exchange O2 and CO2 through diffusion on both sides of the hollow fiber membrane wall, avoiding the direct contact between blood and gas. contact, reducing the denaturation of serum proteins.
Thermostat: It adopts PET capillary tube. When the product is used, blood flows outside the capillary tube and water flows inside. The temperature of the water is adjusted through an external variable temperature water tank, thereby achieving blood temperature control.
Intuitive & Clear Circuitry:The oxygenator for CPB is designed for intuitive operation, with clearly defined blood, gas, and water pathways to prevent misconnections.
Vortex-Enhanced Oxygenation:A vortex blood path ensures maximum gas exchange efficiency with a minimized membrane surface area.
Transparent Design: With individual design and excellent visualization, fault can be found early.
Compliant with EU Standards: The product design and production process comply with European standards.
DEHP-Free Construction:It is built with DEHP-free materials to eliminate the potentia risks.
Thermoregulation:It employs a PET capillary design with external blood flow and internal temperature-controlled water circulation for precise temperature management.
| Specification | WG2500A | WG4000A | WG7000 |
| Venous blood reservoir volume ±10%≥ | 2L | 3L | 4L |
| Minimum injection volume of venous blood reservoir ≤ | 25ml | 35ml | 35ml |
| Minimum safe liquid level ±10% | 200ml | 250ml | 300ml |
| Maximum blood flow (L∕min) | 2.5 | 4 | 7 |
| Oxygenation membrane area ≥ | 1m² | 1.3m² | 1.8m² |
| Temperature changing film area ≥ | 0.25m² | 0.3m² | 0.4m² |
| Precharge amount of blood gas and heat exchange parts ≤ | 160ml | 190ml | 270ml |
| Venous blood inlet size (mm) | 9.5 | 12.7 | 12.7 |
| Arterial blood outlet size (mm) | 9.5或6.3 | 9.5 | 9.5 |
| Recommended patient weight | 10-25kg | 25-40kg | >30kg |
| Heat exchanger inlet and outlet size (mm) | 12.7 (Hansen quick connector) | ||
| Air inlet (mm) | 6.3 | ||
| Recommended gas-blood ratio | 0.5-1:1 | ||
| Blood flow, air flow, water flow clear direction, independent design of each part, excellent visual effects, faults will be discovered as soon as possible |
 |
| The blood flow mode adopts the unique patented design technology of turbine dispersion, and is calculated by fluid dynamics to achieve the minimum membrane area and maximize the oxygenation effect. |
 |
| Detachable blood storage system, closed design, It can be connected to negative pressure auxiliary drainage and has a positive and negative pressure regulating valve. It is currently the only product in China suitable for VAVD surgery. |
 |
| The 360° rotating design of the drainage port is easy and flexible to install. |
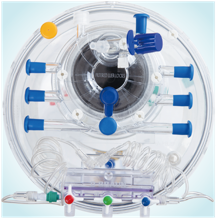 |
| Detachable medicine dosing and blood sample collection device; Safer, faster and more convenient to use |
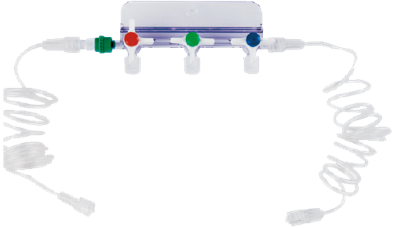 |
| Plug-in fixed bracket, Safe, reliable and easy to operate |
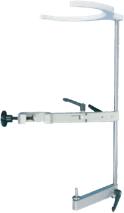 |


WEGO Medical, a subsidiary of Weigao Group, is a leading medical device manufacturer。WEGO Medical, a subsidiary of Weigao Group

WEGO Medical is pleased to announce its participation in WHX Dubai 2026, formerly known as Arab Health, one of the most influential global healthcare exhibitions.

As the new year begins, WEGO Overseas Group would like to extend our warmest New Year greetings to partners, customers, and colleagues around the world.

From all of us at WEGO, we extend our warmest wishes to our global partners and customers. May this festive season bring joy, peace, and
An oxygenator serves as an artificial lung, temporarily taking over the function of the natural lungs by oxygenating the blood and removing carbon dioxide during medical procedures or long-term life support.
An oxygen generator separates and stores oxygen from the air, whereas an oxygen concentrator works by removing nitrogen from the air, thus concentrating the remaining oxygen for delivery.
The duration of oxygenator support is tailored to the patient’s clinical needs. It may be used temporarily for acute recovery or as a long-term solution for chronic conditions, with the treatment timeline determined solely by the healthcare team.
The two primary types of oxygenators are bubble and membrane oxygenators, with the latter being the current clinical standard. Bubble oxygenators, which directly infuse gas into the blood, risk causing hemolysis and microemboli, restricting their use to brief procedures. In contrast, membrane oxygenators employ a gas-permeable barrier that separates blood from gas, significantly reducing blood trauma and enabling safe application in both short-term surgery and prolonged life support.
The use of an oxygenator carries certain risks, which are categorized as follows: fire or explosion hazard due to the combustion-supporting nature of oxygen; clinical complications such as oxygen toxicity, which may manifest as headaches, dizziness, or confusion; and local adverse effects like nasal or throat dryness and irritation.