Oxygenators are medical devices used for life-support surgeries such as cardiopulmonary surgery and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. It can act as an artificial lung for gas exchange, removing carbon dioxide from venous blood and supplementing it with oxygen to ensure that critically ill patients can maintain normal blood oxygen levels during impaired lung function or cardiac surgery.
As a key device in extracorporeal circulatory surgery, understanding the applications, benefits, and potential risks of the oxygenator is essential for healthcare professionals to select and use the device appropriately. The article will cover these in detail. Keep reading for more information!
What is an Oxygenator Used for?
Oxygenators are widely used in the medical field, mainly to support critically ill patients, especially in situations where natural respiration is insufficient to maintain regular blood oxygen levels.
1. Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) is a severe lung injury that causes patients to be unable to perform effective gas exchange on their own, which in turn leads to hypoxemia.
In this case, an oxygenator can partially or completely replace lung function, allowing the blood gas exchange outside the body. This effectively increases the survival chances for ARDS patients and provides more time for pulmonary rehabilitation.
2. Cardiac Surgery
Oxygenators are often used for extracorporeal circulatory support during heart bypass surgery, heart valve replacement or other major heart surgery. It temporarily performs the functions of the lungs and heart to ensure that the patient does not suffer from a lack of oxygen during the procedure and to improve the success rate of the surgery.
3. Treatment of Neonatal or Pediatric Diseases
Some newborns, especially premature babies, may face problems such as Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome (NRDS) or congenital heart disease due to incomplete lung development, resulting in severe hypoxemia. Therefore, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) treatment is required. In addition, membrane oxygenators can also be used for other pediatric critical illnesses, such as poisoning or drowning, to provide stable oxygenation support.
What are the Benefits and Risks of Using Oxygenators?
Oxygenators provide important support in a variety of surgeries involving cardiopulmonary function. However, while it improves therapeutic efficacy, it also comes with certain risks. Here is a detailed description of its benefits and potential risks:
1. Benefits of Oxygenators
- Support Cardiopulmonary Function:ECMO oxygenators support cardiopulmonary function in patients with impaired lung function or temporary cardiac arrest, preventing life-threatening drops in blood oxygen levels.
- Improve the Surgical Success Rate:Due to stable oxygenation support, the oxygenator ensures proper oxygenation of organs during surgery, thus dramatically improving the surgical success rate and making complex cardiac surgery possible.
- Reduce the Risk of Postoperative Complications:Postoperative hypoxemia, organ hypoxia, and multiple organ failure are common complications in surgery. Oxygenator membrane can help minimize brain damage, renal impairment and other complications caused by insufficient oxygen supply, and help patients recover faster.
2. Risks of Oxygenators
Although ECMO machines have shown many advantages, the risks involved cannot be ignored.
- Coagulation Dysfunction:The contact of blood with the oxygenator surface may trigger the coagulation reaction, leading to thrombus formation, which in turn may cause blockages of the blood vessels or other complications. Patients will require anticoagulation therapy.
- Hemolysis Risk:During membrane oxygenator operation, contact of blood with the artificial material may result in the rupture of red blood cells (hemolysis). Hemolysis risk is closely related to the quality of the device, the rate of blood flow, and the operating technique. Therefore, it requires close monitoring of blood status during the surgery.
- Risk of Infection:Any contamination of equipment or unqualified aseptic operation may lead to bacterial infection or sepsis. This emphasizes the importance of aseptic practices and high-quality blood oxygenators.
Risks such as coagulation dysfunctions, hemolysis and infections should not be ignored. Closely monitoring the patient’s condition, optimizing the anticoagulation strategy, using strict asepsis, and choosing high-quality oxygenators are the keys to reducing the risks and improving the surgery success rate.
Where to Order High-quality Oxygenators?
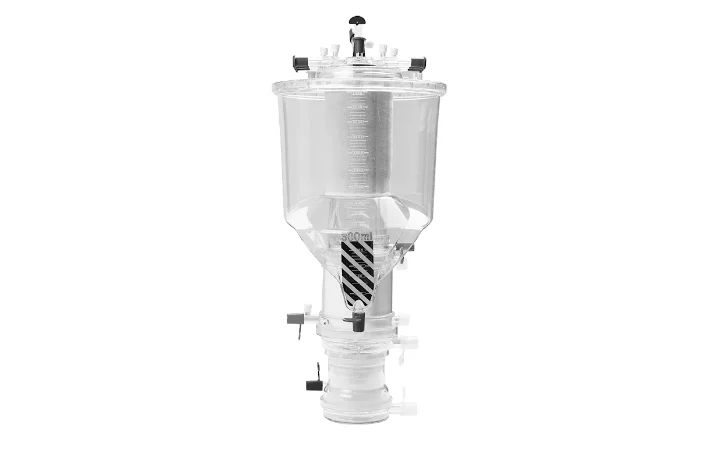
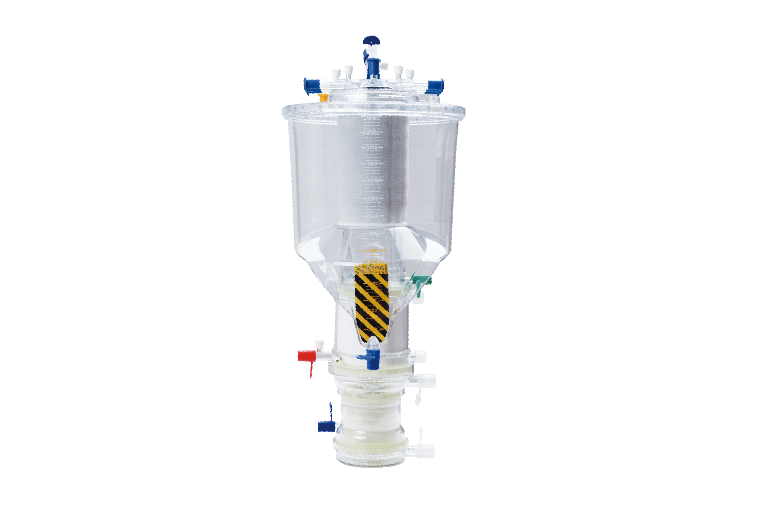
If you are choosing a reliable oxygenator supplier for your healthcare organization, then WEGO Medical is a recommended choice. We understand hospitals’ need for qualified, efficient and safe membrane oxygenators. Our ISO and CE-certified oxygenator excels in VAVD use, oxygenation performance, CO2 removal, and blood compatibility.
Its transparent appearance clearly shows the direction of blood flow, airflow, and water flow for easy troubleshooting. The blood flow mode adopts the unique patented design technology of turbine dispersion to achieve minimum membrane area and maximize the oxygenation effect. In addition, it adopts a detachable blood storage system and a fully enclosed design to effectively prevent contamination.
The 360° rotating design of the drain port, detachable dosing and blood collection device and the plug-in fixed bracket provide convenience for the surgical process.
Conclusion
Overall, the ECMO oxygenator has an indispensable role in the treatment of ARDS, cardiac surgery and pediatric diseases. They support cardiopulmonary function, increase the success rate of surgery and reduce the potential risk of postoperative complications.
However, care must be taken to avoid the risks of coagulation, hemolysis and infection during use. WEGO Medical produces qualified and safe blood oxygenators to avoid device-related risks during surgery. Contact us now to know specifics!