Phlebotomy protocols establish a specific sequence for filling blood collection tubes to protect sample integrity. This procedure, known as the blood collection tubes order of draw, is not arbitrary but is grounded in preventing cross-contamination between tube additives. Following the correct sequence ensures that chemical additives from one tube do not carry over into the next via the needle, which could compromise test results. Adherence to this standard is a fundamental aspect of quality laboratory practice.
Prioritizing Blood Culture and Coagulation Samples
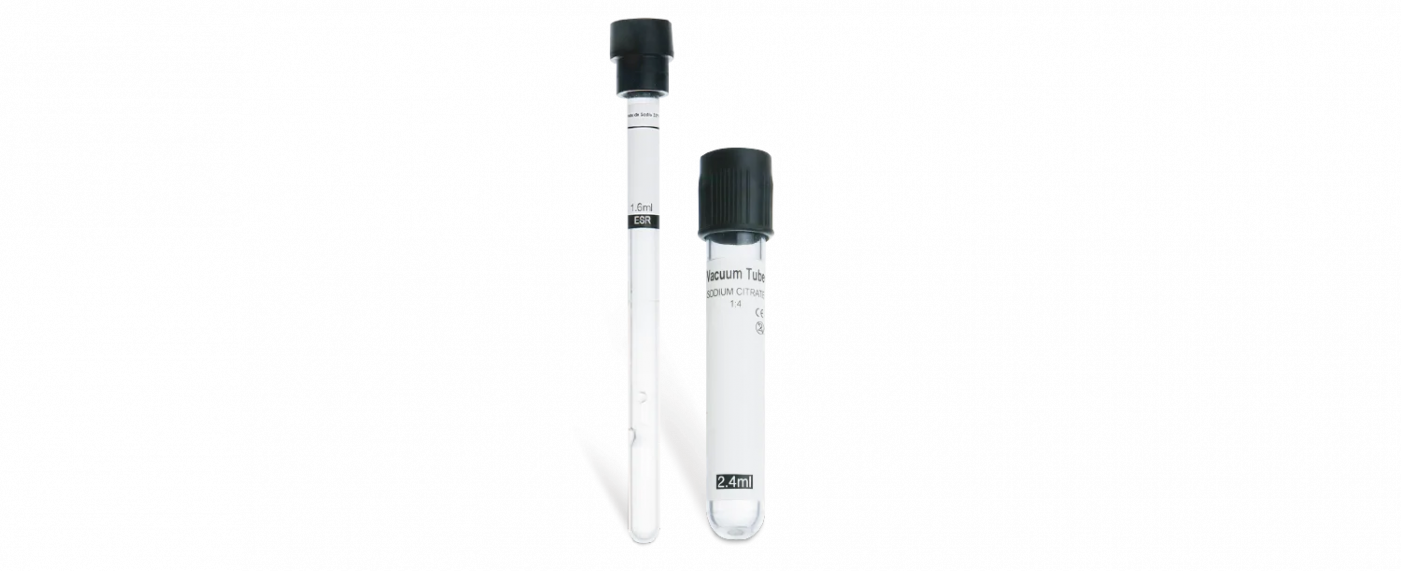
The protocol begins with collecting samples where absolute purity is most critical. Blood culture bottles are drawn first to prevent any microbial contamination from the skin or other sources. Immediately following are tubes designed for coagulation studies, such as light blue-top tubes containing sodium citrate. These are used for tests like PT and PTT, where even tiny amounts of clot activators or other additives can significantly alter the results. Placing these tubes early in the blood collection tubes order of draw minimizes the risk of additive transfer that could invalidate sensitive coagulation assays.
Navigating Tubes with Clot Activators and Serums
The middle of the sequence typically includes tubes without anticoagulants. Red-top or gold-top tubes, which may contain a clot activator and a gel for serum separation, are filled at this stage. Drawing them after the coagulation tubes prevents clot activators from interfering with the citrate in the previous tubes. The serum obtained from these tubes is used for a wide array of chemistry tests, including metabolic panels and enzyme assays, making their purity essential for an accurate diagnosis.
Completing the Draw with Anticoagulant Tubes
The final tubes in the sequence are those containing anticoagulants like EDTA (lavender-top) and heparin (green-top). EDTA is essential for hematology tests, such as complete blood counts, as it preserves cellular morphology. Heparinized plasma is often used for certain chemistry tests. Drawing these last ensures that their potent anticoagulants do not contaminate earlier tubes meant for coagulation or serum studies. This structured conclusion to the blood collection tubes order of draw safeguards the accuracy of a broad spectrum of laboratory analyses.
In our work at WEGO Medical, we produce a range of tubes that fit into this standardized sequence. Our manufacturing process focuses on the precise formulation of additives and the integrity of the vacuum seal, providing phlebotomists with reliable tools for every step of the established protocol.
Mastering the sequence for drawing blood tubes is a key component of clinical competency. This procedure, built on a clear understanding of additive interactions, directly supports diagnostic accuracy. Consistent application of the guidelines ensures that laboratory results truly reflect the patient’s physiological state, forming a reliable basis for clinical decisions.