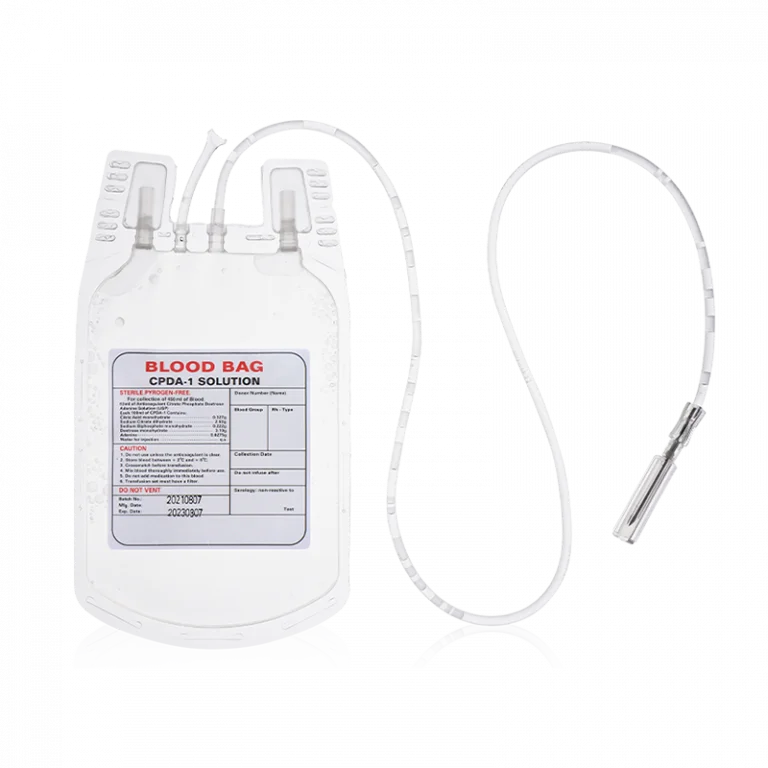
In our daily operations at WEGO Medical, we work closely with hospitals and blood centers to ensure safe and effective blood collection and storage. One of the key aspects we focus on is the choice of anticoagulants in blood bags, as they play a vital role in maintaining blood quality over time. Among the most commonly used anticoagulants are CPDA-1, CPD, and ACD, each with distinct characteristics that influence how blood is collected, stored, and transfused. For instance, when using a CPDA-1 single blood bag, we can preserve red blood cells for longer periods, making it particularly useful for blood banks that need extended storage capabilities.
Comparing CPDA-1, CPD, and ACD
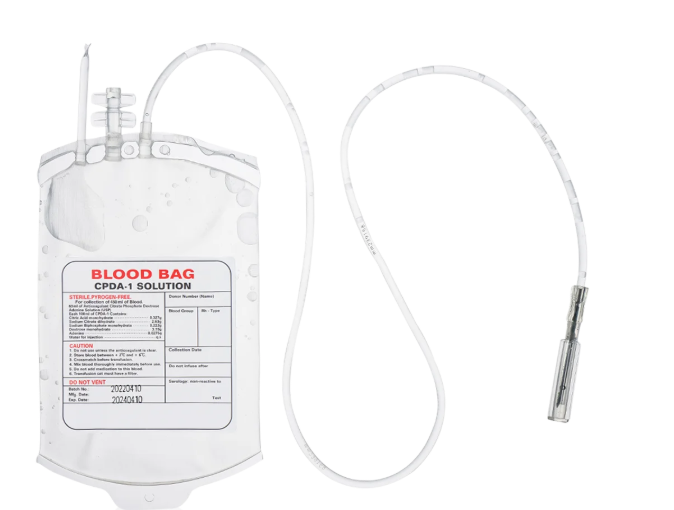
From our experience, the differences among CPDA-1, CPD, and ACD primarily lie in their composition and storage duration. CPDA-1 single blood bag contains citrate, phosphate, dextrose, and adenine, which helps maintain red blood cell viability for up to 35 days under proper refrigeration. CPD, on the other hand, lacks adenine, so its storage life is slightly shorter, typically around 21 days. ACD, which contains acid-citrate-dextrose, is mainly used for shorter-term storage and procedures such as platelet collection or whole blood transfusions that need to be completed within a few days. We often guide our partners in selecting the appropriate anticoagulant based on their operational needs and transfusion requirements, ensuring optimal outcomes for both patients and blood centers.
Practical Considerations in Blood Collection
In our work, we notice that choosing the right anticoagulant is not only about storage duration but also about the type of blood component required. Using a CPDA-1 single blood bag allows us to collect whole blood that can be separated later into red cells, plasma, and platelets with minimal degradation. Meanwhile, CPD and ACD are more suited for situations where shorter storage or immediate processing is necessary. We provide guidance on handling, labeling, and storage conditions to maximize the shelf life and functionality of each blood unit, which is essential in maintaining safety and efficacy in transfusions.
Conclusion
Overall, understanding the differences between CPDA-1, CPD, and ACD is essential for efficient blood management. At WEGO Medical, we prioritize providing solutions that help healthcare institutions make informed decisions about anticoagulants. By choosing the correct blood bag system, such as the CPDA-1 single blood bag, we can support longer storage and maintain blood quality, which ultimately benefits both healthcare providers and patients. We continuously collaborate with our partners to offer professional guidance and high-quality products that meet the diverse needs of modern blood banks and hospitals.